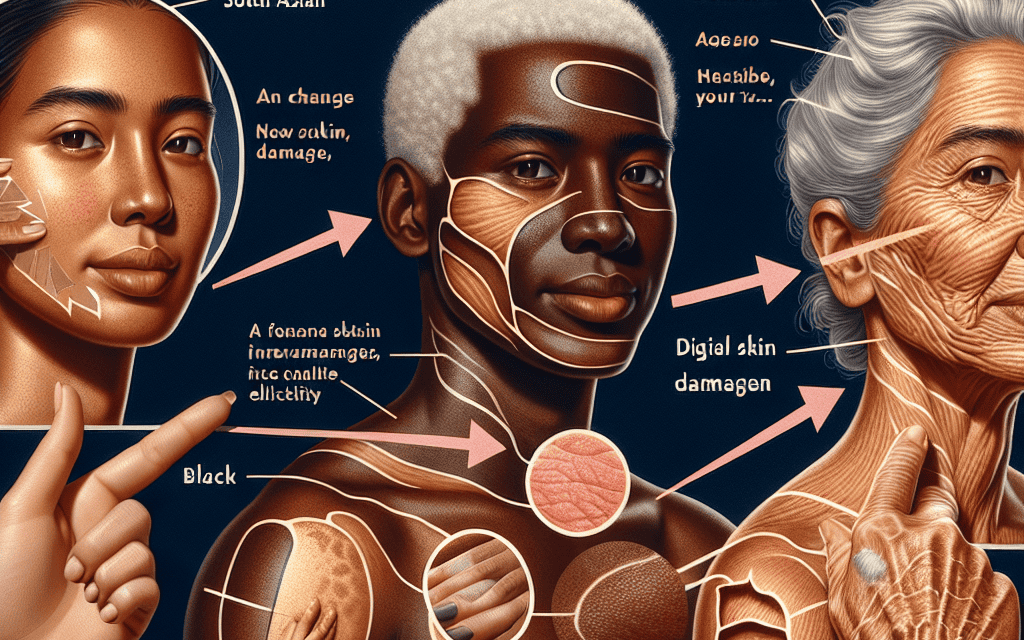
Understanding Your Skin: Key Changes to Notice
Our skin is not just a protective barrier; it is a dynamic organ that reflects our overall health and well-being. As we age, our skin undergoes various changes influenced by genetics, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices. Understanding these changes is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and addressing any concerns that may arise. This article delves into the key changes to notice in your skin, providing insights into their causes, implications, and how to manage them effectively.
1. The Aging Process: What to Expect
As we age, our skin naturally undergoes a series of transformations. These changes can be attributed to intrinsic factors (genetics and biological aging) and extrinsic factors (sun exposure, pollution, and lifestyle). Understanding these changes can help you take proactive steps to maintain your skin’s health.
Intrinsic Aging
Intrinsic aging, also known as chronological aging, is the natural aging process that occurs regardless of external factors. It typically begins in our 20s and accelerates in our 40s and beyond. Key characteristics of intrinsic aging include:
- Thinning Skin: The dermis, which contains collagen and elastin, begins to thin, leading to a loss of firmness and elasticity.
- Decreased Oil Production: Sebaceous glands produce less oil, resulting in drier skin.
- Reduced Cell Turnover: The rate of skin cell turnover slows down, leading to a dull complexion.
These changes can lead to the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and sagging skin. A study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology found that the skin loses approximately 1% of its collagen each year after the age of 20, contributing to these visible signs of aging.
Extrinsic Aging
Extrinsic aging is influenced by environmental factors and lifestyle choices. The most significant contributor is sun exposure, which can lead to photoaging. Key signs of extrinsic aging include:
- Sunspots: Also known as age spots or liver spots, these are flat, brown spots that develop on sun-exposed areas of the skin.
- Wrinkles and Fine Lines: UV radiation breaks down collagen and elastin, leading to premature wrinkles.
- Uneven Skin Tone: Sun damage can cause hyperpigmentation, resulting in a blotchy complexion.
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, up to 90% of visible skin changes attributed to aging are caused by sun exposure. Protecting your skin from the sun is crucial for preventing these changes.
2. Changes in Skin Texture and Tone
As we age, our skin’s texture and tone can change significantly. These changes can be influenced by various factors, including hormonal fluctuations, environmental exposure, and lifestyle choices.
Texture Changes
Skin texture can become rough and uneven due to several factors:
- Decreased Collagen Production: As collagen production declines with age, skin may feel less firm and smooth.
- Accumulation of Dead Skin Cells: Slower cell turnover can lead to a buildup of dead skin cells, resulting in a rough texture.
- Environmental Damage: Pollution and UV exposure can contribute to a rough skin surface.
To improve skin texture, consider incorporating exfoliation into your skincare routine. Chemical exfoliants, such as alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs), can help remove dead skin cells and promote a smoother complexion.
Tone Changes
Skin tone can also change due to various factors:
- Hyperpigmentation: Sun exposure and hormonal changes can lead to dark spots and uneven skin tone.
- Rosacea and Redness: Conditions like rosacea can cause persistent redness and flushing.
- Age-Related Changes: The skin may become paler or develop a yellowish tint due to decreased blood flow and changes in fat distribution.
To address tone changes, consider using products with ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, and retinoids, which can help brighten the skin and reduce hyperpigmentation.
3. The Impact of Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can significantly impact the skin, particularly during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. Understanding these changes can help you manage skin concerns effectively.
Puberty and Adolescence
During puberty, increased levels of androgens (male hormones) can lead to various skin changes:
- Increased Oil Production: Androgens stimulate sebaceous glands, leading to oily skin and acne.
- Acne Development: The combination of excess oil and clogged pores can result in acne breakouts.
- Changes in Skin Texture: Skin may become thicker and more prone to blemishes.
Managing acne during adolescence often involves a combination of topical treatments (like benzoyl peroxide and salicylic acid) and lifestyle changes (such as a balanced diet and proper skincare).
Menstrual Cycle
Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can also affect the skin:
- Pre-Menstrual Breakouts: Many women experience acne flare-ups in the days leading up to their period due to increased progesterone levels.
- Changes in Oiliness: Skin may become oilier or drier depending on hormonal shifts.
- Increased Sensitivity: Some women may notice heightened skin sensitivity during certain phases of their cycle.
Keeping a consistent skincare routine and using non-comedogenic products can help manage these fluctuations.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy brings about significant hormonal changes that can affect the skin:
- Pregnancy Glow: Increased blood flow and hormonal changes can lead to a radiant complexion for some women.
- Melasma: Hormonal changes can cause dark patches on the face, known as the “mask of pregnancy.”
- Stretch Marks: Rapid skin stretching can lead to the development of stretch marks on the abdomen, breasts, and thighs.
To manage pregnancy-related skin changes, consider using gentle skincare products and consulting with a dermatologist for safe treatment options.
Menopause
Menopause brings about a decline in estrogen levels, leading to various skin changes:
- Dryness: Reduced oil production can lead to dry, flaky skin.
- Loss of Elasticity: Decreased collagen levels can result in sagging skin and wrinkles.
- Increased Sensitivity: Some women may experience increased skin sensitivity and conditions like rosacea.
To combat menopause-related skin changes, consider using hydrating products, retinoids, and antioxidants to support skin health.
4. Environmental Factors and Their Effects
Environmental factors play a significant role in skin health. Understanding how these factors affect your skin can help you take preventive measures.
Sun Exposure
Sun exposure is one of the most significant contributors to skin damage. Key effects of UV radiation include:
- Photoaging: UV rays break down collagen and elastin, leading to wrinkles and sagging skin.
- Skin Cancer: Prolonged sun exposure increases the risk of skin cancer, including melanoma.
- Hyperpigmentation: Sun exposure can lead to dark spots and uneven skin tone.
To protect your skin from sun damage, use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during peak sun hours.
Pollution
Air pollution can have detrimental effects on the skin:
- Oxidative Stress: Pollutants can generate free radicals, leading to premature aging and skin damage.
- Inflammation: Pollution can trigger inflammatory responses, exacerbating conditions like acne and eczema.
- Clogged Pores: Dirt and pollutants can accumulate on the skin, leading to clogged pores and breakouts.
To combat pollution-related skin issues, consider using antioxidant-rich skincare products and cleansing your skin thoroughly at the end of the day.
Climate
The climate in which you live can also impact your skin:
- Humidity: High humidity can lead to excess oil production, while low humidity can cause dryness.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can exacerbate skin conditions like eczema and rosacea.
- Seasonal Changes: Skin may require different care routines in summer versus winter due to varying environmental conditions.
Adapting your skincare routine to suit the climate can help maintain skin health. For example, use heavier moisturizers in winter and lightweight formulas in summer.
5. Lifestyle Choices and Their Impact on Skin Health
Your lifestyle choices can significantly influence your skin’s appearance and health. Understanding these factors can empower you to make informed decisions for better skin.
Diet
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in skin health:
- Hydration: Drinking enough water helps maintain skin hydration and elasticity.
- Antioxidants: Foods rich in antioxidants (like fruits and vegetables) can combat oxidative stress and promote healthy skin.
- Healthy Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and nuts can help maintain skin barrier function.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that a diet high in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats is associated with better skin health and reduced signs of aging.
Exercise
Regular physical activity can benefit your skin in several ways:
- Improved Circulation: Exercise increases blood flow, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the skin.
- Stress Reduction: Physical activity can reduce stress levels, which can positively impact skin conditions like acne and eczema.
- Detoxification: Sweating during exercise helps remove toxins from the skin.
Incorporating regular exercise into your routine can contribute to a healthier complexion and overall well-being.
Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for skin health:
- Cell Regeneration: During sleep, the body repairs and regenerates skin cells, promoting a healthy complexion.
- Stress Management: Lack of sleep can increase stress hormones, leading to skin issues like acne and inflammation.
- Dark Circles: Insufficient sleep can result in dark circles and puffiness around the eyes.
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support your skin’s health and appearance.
Skincare Routine
A consistent skincare routine is vital for maintaining healthy skin:
- Cleansing: Regular cleansing helps remove dirt, oil, and makeup, preventing clogged pores.
- Moisturizing: Hydrating the skin helps maintain its barrier function and prevents dryness.
- Sun Protection: Daily sunscreen application is crucial for preventing sun damage and premature aging.
Consulting with a dermatologist can help you develop a personalized skincare routine tailored to your skin type and concerns.
Conclusion
Understanding your skin and the key changes it undergoes throughout life is essential for maintaining its health and appearance. From the natural aging process to the impact of environmental factors and lifestyle choices, being aware of these changes empowers you to take proactive steps in your skincare journey. By recognizing the signs of aging, hormonal fluctuations, environmental damage, and the importance of a healthy lifestyle, you can make informed decisions that promote radiant, healthy skin.
In summary, here are the key takeaways:
- Intrinsic and extrinsic aging significantly impact skin health, with sun exposure being a major contributor to visible signs of aging.
- Changes in skin texture and tone can be managed through proper exfoliation and the use of brightening ingredients.
- Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can lead to various skin concerns that require tailored management strategies.
- Environmental factors such as pollution and climate can affect skin health, necessitating protective measures in your skincare routine.
- Lifestyle choices, including diet, exercise, sleep, and a consistent skincare routine, play a crucial role in maintaining healthy skin.
By staying informed and proactive, you can navigate the complexities of skin changes and enjoy a lifetime of healthy, glowing skin.