Understanding Your Gum Health: What It Reveals About Your Overall Well-Being
Gum health is often overlooked in discussions about overall health, yet it plays a crucial role in our well-being. The condition of your gums can reveal a lot about your general health, including potential risks for systemic diseases. This article delves into the intricate relationship between gum health and overall well-being, exploring various aspects that highlight the importance of maintaining healthy gums.
The Anatomy of Gum Health
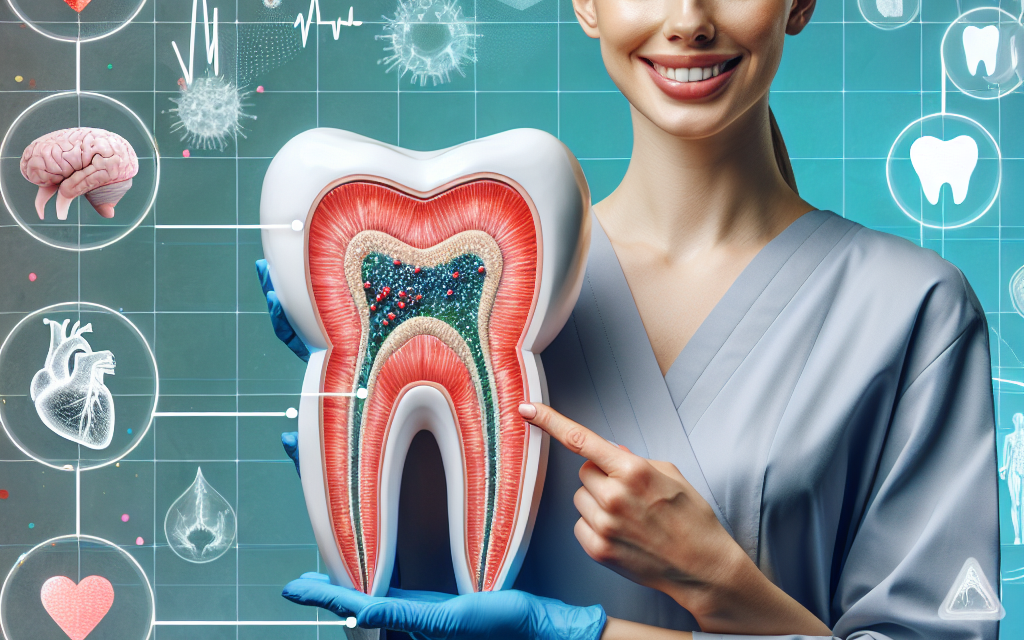
To understand gum health, it is essential to first grasp the anatomy of the gums and their role in oral health. The gums, or gingiva, are the soft tissues that surround and support the teeth. They serve as a barrier against bacteria and other harmful substances, protecting the underlying bone and tooth roots.
Healthy gums are typically pink, firm, and do not bleed during brushing or flossing. However, when gum disease occurs, the gums can become inflamed, swollen, and may bleed easily. The two primary stages of gum disease are gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Gingivitis: This is the initial stage of gum disease, characterized by inflammation of the gums. It is often caused by plaque buildup and can be reversed with proper oral hygiene.
- Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe condition that can lead to tooth loss and has been linked to systemic health issues.
Understanding the anatomy and function of the gums is crucial for recognizing the signs of gum disease and taking proactive steps to maintain gum health. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices are essential for preventing gum disease and ensuring overall well-being.
The Link Between Gum Health and Systemic Diseases
Research has increasingly shown that gum health is closely linked to various systemic diseases. Poor gum health can be both a risk factor and a consequence of several health conditions. Here are some of the most significant connections:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Studies have found that individuals with gum disease are at a higher risk for heart disease. The inflammation caused by gum disease can contribute to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to cardiovascular issues.
- Diabetes: There is a bidirectional relationship between diabetes and gum disease. People with diabetes are more susceptible to infections, including gum disease, while gum disease can make it more challenging to control blood sugar levels.
- Respiratory Diseases: Bacteria from the mouth can be inhaled into the lungs, potentially leading to respiratory infections. This is particularly concerning for individuals with pre-existing lung conditions.
- Pregnancy Complications: Pregnant women with gum disease may be at a higher risk for preterm birth and low birth weight babies. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can exacerbate gum issues.
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Emerging research suggests a link between gum disease and cognitive decline. Chronic inflammation from gum disease may contribute to the development of Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia.
These connections highlight the importance of maintaining good gum health not just for oral hygiene but for overall health. Regular dental visits and good oral hygiene practices can help mitigate these risks.
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of gum disease is crucial for early intervention. Many people may not realize they have gum disease until it has progressed significantly. Here are some common signs to watch for:
- Bleeding Gums: One of the most common signs of gum disease is bleeding during brushing or flossing. Healthy gums should not bleed.
- Swollen or Red Gums: Inflammation is a key indicator of gum disease. Gums that appear swollen or red may be a sign of gingivitis.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath, or halitosis, can be a sign of gum disease, as bacteria build up in the mouth.
- Receding Gums: If your gums appear to be pulling away from your teeth, this could indicate gum disease and the need for professional evaluation.
- Loose Teeth: Advanced gum disease can lead to tooth mobility due to the loss of supporting bone structure.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a dental professional for an evaluation. Early detection and treatment can prevent the progression of gum disease and its associated health risks.
Preventive Measures for Maintaining Gum Health
Preventing gum disease is far more effective than treating it after it has developed. Here are several preventive measures that can help maintain healthy gums:
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visiting your dentist at least twice a year for cleanings and check-ups can help catch gum disease early.
- Proper Oral Hygiene: Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily are essential practices for maintaining gum health.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, can support gum health. Foods high in sugar can contribute to plaque buildup.
- Avoid Tobacco Products: Smoking and other tobacco use are significant risk factors for gum disease. Quitting can greatly improve gum health.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections, including gum disease.
Incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine can significantly reduce the risk of developing gum disease and improve your overall health.
The Role of Nutrition in Gum Health
Nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining gum health. A well-balanced diet can provide the necessary nutrients to support the immune system and promote healing. Here are some key nutrients that are particularly beneficial for gum health:
- Vitamin C: This vitamin is essential for collagen production, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of gum tissue. A deficiency in vitamin C can lead to gum disease.
- Calcium: Calcium is vital for maintaining strong teeth and bones. It helps support the structure of the jawbone and can prevent tooth loss.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These healthy fats have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce gum inflammation and promote healing.
- Antioxidants: Foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can help combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the gums.
- Probiotics: Emerging research suggests that probiotics may help balance oral bacteria and reduce the risk of gum disease.
Incorporating these nutrients into your diet can support gum health and overall well-being. Foods such as citrus fruits, leafy greens, nuts, fish, and yogurt are excellent choices for promoting healthy gums.
Conclusion
Understanding your gum health is crucial for maintaining overall well-being. The condition of your gums can reveal important insights into your general health, including potential risks for systemic diseases. By recognizing the signs of gum disease, taking preventive measures, and maintaining a healthy diet, you can significantly improve your gum health and, consequently, your overall health.
Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices are essential for preventing gum disease and its associated health risks. Remember, healthy gums are not just about a beautiful smile; they are a vital component of your overall health. Prioritizing your gum health can lead to a healthier, happier life.