Understanding the Rise of Bunions and Effective Solutions
Bunions, medically known as hallux valgus, are a common foot deformity characterized by a bony bump that forms at the base of the big toe. This condition can lead to pain, discomfort, and difficulty in finding suitable footwear. The rise in bunion cases has become a significant concern in recent years, prompting a need for a deeper understanding of the factors contributing to their prevalence and the effective solutions available for management and treatment. This article will explore the causes of bunions, their impact on daily life, preventive measures, treatment options, and the role of footwear in bunion development.
1. The Anatomy of Bunions: Understanding the Condition
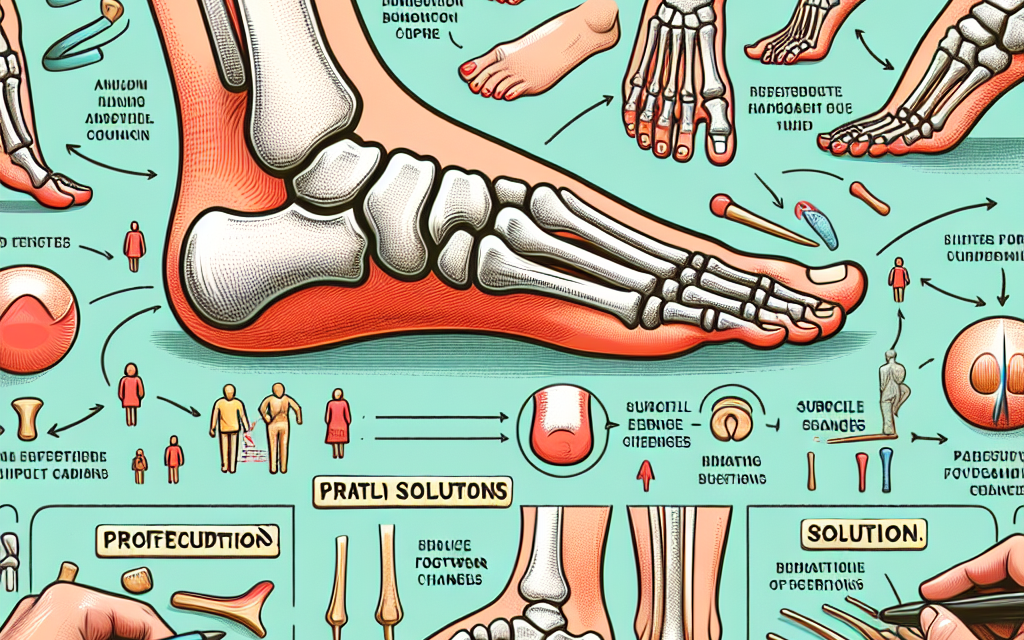
Bunions develop when the big toe deviates towards the second toe, causing the first metatarsal bone to protrude. This misalignment can lead to a variety of symptoms, including pain, swelling, and difficulty walking. Understanding the anatomy of bunions is crucial for grasping how they develop and the implications they have on foot health.
The foot consists of 26 bones, 33 joints, and over 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The big toe, or hallux, plays a vital role in maintaining balance and stability while walking. When a bunion forms, the normal alignment of the bones is disrupted, leading to a cascade of biomechanical changes. The following factors contribute to the development of bunions:
- Genetics: A family history of bunions can increase the likelihood of developing this condition. Genetic predisposition affects the structure of the foot and the way weight is distributed across it.
- Footwear Choices: Wearing tight, narrow shoes can exacerbate bunion formation. High heels and pointed-toe shoes place undue pressure on the toes, leading to misalignment.
- Foot Structure: Individuals with flat feet or low arches are more susceptible to bunions due to the altered mechanics of their feet.
- Age: As people age, the ligaments and tendons in the foot can weaken, increasing the risk of bunion development.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as arthritis can contribute to the formation of bunions by affecting joint stability.
Understanding these anatomical and physiological factors is essential for both prevention and treatment. By recognizing the early signs of bunions, individuals can take proactive steps to mitigate their development.
2. The Impact of Bunions on Daily Life
Bunions can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. The pain and discomfort associated with bunions can lead to limitations in mobility and daily activities. Understanding the impact of bunions on daily life is crucial for recognizing the importance of seeking treatment.
Many individuals with bunions experience chronic pain, which can be exacerbated by prolonged standing or walking. This discomfort can lead to a reluctance to engage in physical activities, resulting in a sedentary lifestyle. The psychological effects of living with bunions can also be profound. Many individuals report feelings of embarrassment or self-consciousness about the appearance of their feet, which can lead to social withdrawal.
Moreover, bunions can affect footwear choices, forcing individuals to opt for less stylish but more comfortable shoes. This can further impact self-esteem and body image. The financial burden of managing bunions can also be significant, as individuals may need to invest in specialized footwear, orthotics, or even surgical interventions.
Case studies illustrate the real-life implications of bunions:
- Case Study 1: A 45-year-old woman with a family history of bunions developed severe pain in her left foot, making it difficult to participate in her favorite activities, such as hiking and dancing. After consulting with a podiatrist, she learned about the importance of proper footwear and began using orthotic inserts, which alleviated her pain and allowed her to return to her active lifestyle.
- Case Study 2: A 60-year-old man experienced chronic pain due to bunions, which led to a decline in his physical health. After undergoing surgery to correct the alignment of his toes, he reported a significant improvement in his quality of life, allowing him to engage in activities he had previously avoided.
These examples highlight the multifaceted impact of bunions on individuals’ lives, emphasizing the need for effective solutions and interventions.
3. Preventive Measures: How to Avoid Bunions
Preventing bunions is possible through a combination of lifestyle changes, proper footwear choices, and foot care practices. Understanding these preventive measures can help individuals reduce their risk of developing bunions.
One of the most effective ways to prevent bunions is to choose appropriate footwear. Shoes that provide ample room for the toes, a wide toe box, and adequate arch support can help maintain proper foot alignment. Here are some tips for selecting the right footwear:
- Avoid Tight Shoes: Shoes that pinch the toes or place excessive pressure on the forefoot should be avoided. Opt for shoes that allow for natural toe splay.
- Choose Low Heels: High-heeled shoes can exacerbate bunion formation. If heels are necessary, limit their height and choose styles with a wider toe box.
- Consider Orthotics: Custom orthotic inserts can provide additional support and cushioning, helping to maintain proper foot alignment.
- Wear Supportive Sandals: When choosing sandals, look for styles with arch support and adjustable straps to accommodate foot swelling.
In addition to footwear choices, regular foot care is essential for preventing bunions. This includes:
- Stretching Exercises: Regularly stretching the toes and feet can improve flexibility and reduce the risk of misalignment.
- Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening the muscles in the feet can help maintain proper alignment and support.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can place additional stress on the feet, increasing the risk of bunion development.
By incorporating these preventive measures into daily life, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing bunions and maintain better overall foot health.
4. Treatment Options: Managing Bunions Effectively
For individuals who already have bunions, various treatment options are available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Understanding these options is crucial for making informed decisions about care.
Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of defense against bunions. These may include:
- Orthotic Devices: Custom orthotics can help redistribute pressure on the foot and improve alignment, alleviating pain associated with bunions.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen foot muscles and improve flexibility.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and inflammation associated with bunions.
In cases where non-surgical treatments are ineffective, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options for bunion correction include:
- Osteotomy: This procedure involves cutting and realigning the bones in the foot to correct the deformity.
- Exostectomy: This surgery removes the bony bump on the toe but does not address the underlying misalignment.
- Arthrodesis: This procedure fuses the bones in the affected joint to provide stability and reduce pain.
Case studies highlight the effectiveness of these treatments:
- Case Study 1: A 50-year-old woman underwent physical therapy and used orthotic devices for several months. While her symptoms improved, she ultimately opted for surgery when conservative measures failed to provide sufficient relief.
- Case Study 2: A 30-year-old man with a severe bunion underwent an osteotomy and reported significant pain relief and improved foot function post-surgery.
Ultimately, the choice of treatment depends on the severity of the bunion, the level of pain experienced, and the individual’s lifestyle and preferences. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for determining the most appropriate course of action.
5. The Role of Footwear in Bunion Development
Footwear plays a critical role in both the development and management of bunions. Understanding how shoes can contribute to or alleviate this condition is essential for making informed choices about footwear.
As previously mentioned, tight and narrow shoes can exacerbate bunion formation. The pressure exerted on the toes can lead to misalignment and increased pain. Here are some key considerations regarding footwear:
- Toe Box Width: Shoes with a wide toe box allow for natural toe splay, reducing pressure on the bunion and preventing further deformity.
- Arch Support: Proper arch support helps maintain foot alignment and reduces strain on the ligaments and tendons.
- Material: Soft, flexible materials can accommodate foot swelling and provide comfort, while rigid materials can exacerbate discomfort.
- Heel Height: Low-heeled shoes are generally more favorable for individuals with bunions, as they reduce pressure on the forefoot.
Case studies illustrate the impact of footwear on bunion management:
- Case Study 1: A 40-year-old woman switched to shoes with a wider toe box and arch support after experiencing pain from her bunions. She reported a significant reduction in discomfort and an improvement in her ability to walk long distances.
- Case Study 2: A 55-year-old man continued to wear narrow dress shoes despite his bunion diagnosis. His condition worsened, leading to increased pain and difficulty walking. After transitioning to more supportive footwear, he experienced relief and improved mobility.
In conclusion, the role of footwear in bunion development cannot be overstated. By making informed choices about shoes, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing bunions and manage existing conditions more effectively.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways on Bunions and Their Management
Bunions are a prevalent foot condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the anatomy of bunions, their impact on daily life, preventive measures, treatment options, and the role of footwear is essential for effective management. Key takeaways from this article include:
- Bunions develop due to a combination of genetic, structural, and lifestyle factors.
- The impact of bunions extends beyond physical discomfort, affecting emotional well-being and social interactions.
- Preventive measures, including proper footwear choices and foot care practices, can significantly reduce the risk of developing bunions.
- Non-surgical treatments are often effective for managing bunion symptoms, but surgical options may be necessary for severe cases.
- Footwear plays a critical role in both the development and management of bunions, making informed choices essential.
By taking proactive steps to understand and manage bunions, individuals can improve their foot health and overall quality of life. Consulting with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options is crucial for effective management of this common condition.