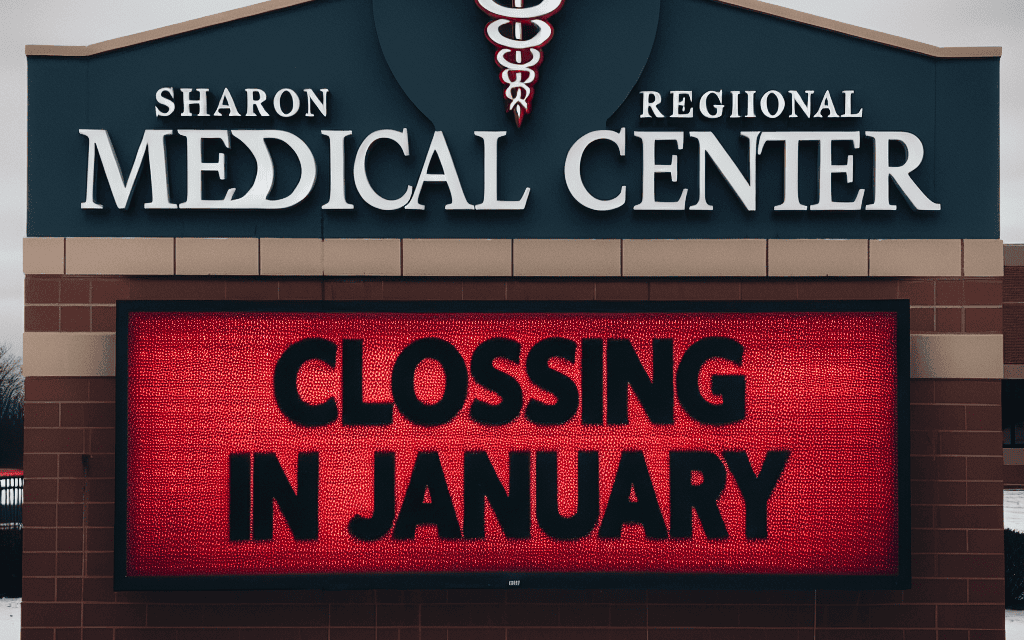
Steward Health Care to Shut Down Sharon Regional Medical Center in January
The impending closure of Sharon Regional Medical Center (SRMC) by Steward Health Care has sent shockwaves through the local community and the healthcare landscape in Pennsylvania. As one of the primary healthcare providers in the region, the shutdown raises significant concerns about access to medical services, the economic impact on the community, and the broader implications for healthcare delivery in rural areas. This article delves into the reasons behind the closure, its potential consequences, and the future of healthcare in the region.
1. Background of Sharon Regional Medical Center
Sharon Regional Medical Center has been a cornerstone of healthcare in the Shenango Valley since its establishment. Originally founded in 1890, the facility has undergone numerous transformations, expanding its services and adapting to the changing needs of the community. Over the years, SRMC has provided a wide range of medical services, including emergency care, surgical services, and specialized treatments.
Despite its long-standing history and commitment to patient care, SRMC has faced numerous challenges in recent years. These challenges include financial difficulties, competition from larger healthcare systems, and changes in healthcare policy that have affected reimbursement rates. The hospital’s struggle to maintain profitability has been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which placed unprecedented strain on healthcare resources nationwide.
In 2018, Steward Health Care acquired SRMC, promising to invest in the facility and improve its services. However, the anticipated improvements did not materialize as expected, leading to ongoing financial losses. The decision to close the hospital in January 2024 marks a significant shift in the healthcare landscape of the region, leaving many residents concerned about their access to essential medical services.
2. Reasons for the Closure
The decision to shut down Sharon Regional Medical Center is rooted in a combination of financial, operational, and strategic factors. Understanding these reasons is crucial to grasping the broader implications of the closure.
- Financial Struggles: SRMC has been operating at a loss for several years, with mounting debts and insufficient revenue to cover operational costs. The hospital’s financial difficulties have been compounded by declining patient volumes and increased competition from larger healthcare systems.
- Impact of COVID-19: The pandemic significantly affected healthcare facilities across the country, and SRMC was no exception. The hospital faced increased costs related to COVID-19 preparedness and a decline in elective procedures, which are vital for generating revenue.
- Changes in Healthcare Policy: Reimbursement rates for Medicare and Medicaid have changed, impacting the hospital’s revenue streams. The shift towards value-based care has also placed additional pressure on facilities that struggle to meet quality metrics.
- Competition from Larger Systems: The healthcare landscape has seen a trend towards consolidation, with larger systems acquiring smaller hospitals. SRMC has struggled to compete with these larger entities, which often have more resources and a broader range of services.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Internal management issues and operational inefficiencies have hindered SRMC’s ability to adapt to the changing healthcare environment. The lack of investment in technology and infrastructure has further exacerbated these challenges.
These factors combined have created a perfect storm for SRMC, leading to the difficult decision to close its doors. The implications of this closure extend far beyond the hospital itself, affecting patients, employees, and the community at large.
3. Impact on the Community
The closure of Sharon Regional Medical Center will have profound effects on the local community, particularly in terms of access to healthcare services. For many residents, SRMC has been their primary source of medical care, and its absence will create significant gaps in service delivery.
- Access to Emergency Services: One of the most immediate concerns is the loss of emergency services. SRMC has been a critical provider of emergency care in the region, and its closure will require patients to travel further for emergency treatment, potentially jeopardizing their health outcomes.
- Increased Travel Times: With the nearest hospitals located miles away, residents will face longer travel times for routine and emergency care. This is particularly concerning for vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with chronic conditions who may require frequent medical attention.
- Job Losses: The closure will result in significant job losses for the hospital’s staff, including nurses, doctors, and administrative personnel. This not only affects the individuals directly impacted but also has a ripple effect on the local economy, as these employees contribute to local businesses.
- Economic Impact: The loss of a major employer in the region will have broader economic implications. Local businesses that rely on hospital employees for patronage may suffer, leading to further job losses and economic decline.
- Community Health Outcomes: The closure may lead to poorer health outcomes for the community. Studies have shown that access to healthcare is directly correlated with health outcomes, and the loss of a local hospital could exacerbate existing health disparities.
As the community grapples with these challenges, local leaders and healthcare advocates are calling for solutions to mitigate the impact of the closure. This includes exploring partnerships with nearby hospitals and increasing telehealth services to improve access to care.
4. Alternatives and Solutions
In light of the impending closure of Sharon Regional Medical Center, it is essential to explore potential alternatives and solutions to address the healthcare needs of the community. While the situation is dire, there are several strategies that could help mitigate the impact of the closure.
- Telehealth Services: Expanding telehealth services can provide residents with access to medical consultations without the need for travel. This is particularly beneficial for routine check-ups and follow-up appointments, allowing patients to receive care from the comfort of their homes.
- Partnerships with Nearby Hospitals: Local leaders could explore partnerships with nearby healthcare facilities to ensure that residents have access to essential services. This could involve transferring patients to other hospitals for emergency care or establishing satellite clinics in the community.
- Community Health Initiatives: Investing in community health initiatives can help address some of the health disparities exacerbated by the closure. Programs focused on preventive care, health education, and chronic disease management can improve overall health outcomes.
- Advocacy for Policy Changes: Local advocates can work to influence healthcare policy at the state and federal levels to ensure that rural communities receive adequate support. This includes advocating for better reimbursement rates and funding for rural healthcare facilities.
- Exploring Alternative Care Models: Innovative care models, such as urgent care centers or community health clinics, could be established to fill the gap left by SRMC. These facilities can provide essential services and reduce the burden on emergency departments in nearby hospitals.
While these solutions may not fully replace the services provided by Sharon Regional Medical Center, they can help to alleviate some of the challenges faced by the community. Collaboration among healthcare providers, local leaders, and residents will be crucial in navigating this transition.
5. The Future of Healthcare in Rural Areas
The closure of Sharon Regional Medical Center is part of a larger trend affecting rural healthcare across the United States. As smaller hospitals struggle to remain viable, it raises important questions about the future of healthcare delivery in these areas.
- Consolidation of Healthcare Services: The trend towards consolidation is likely to continue, with larger healthcare systems acquiring smaller hospitals. While this can lead to improved resources and services, it may also result in reduced local control and access to care.
- Telemedicine Expansion: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, and this trend is expected to continue. Telehealth can play a vital role in providing care to rural populations, but it requires investment in technology and infrastructure.
- Policy Advocacy: Advocacy for rural healthcare funding and policy changes will be essential to ensure that rural communities receive the support they need. This includes addressing reimbursement rates and providing incentives for healthcare providers to practice in underserved areas.
- Community Engagement: Engaging the community in discussions about healthcare needs and solutions is crucial. Local residents can provide valuable insights into the services they require and how best to address gaps in care.
- Innovative Care Models: The future of rural healthcare may involve innovative care models that prioritize accessibility and affordability. This could include mobile clinics, community health workers, and partnerships with local organizations to provide comprehensive care.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, it is essential for rural communities to adapt and find solutions that meet their unique needs. The closure of Sharon Regional Medical Center serves as a wake-up call for stakeholders to prioritize the health and well-being of rural populations.
Conclusion
The decision by Steward Health Care to shut down Sharon Regional Medical Center in January 2024 marks a significant turning point for the community and the healthcare landscape in Pennsylvania. The closure is driven by a combination of financial struggles, operational challenges, and the broader trends affecting rural healthcare. As the community faces the consequences of this decision, it is crucial to explore alternatives and solutions to ensure continued access to essential medical services.
While the loss of SRMC will undoubtedly create challenges, it also presents an opportunity for local leaders, healthcare providers, and residents to come together to advocate for innovative solutions that address the healthcare needs of the community. The future of healthcare in rural areas depends on collaboration, advocacy, and a commitment to ensuring that all individuals have access to the care they need.
In summary, the closure of Sharon Regional Medical Center is a complex issue with far-reaching implications. By understanding the reasons behind the closure and exploring potential solutions, stakeholders can work towards a future where healthcare remains accessible and equitable for all residents.