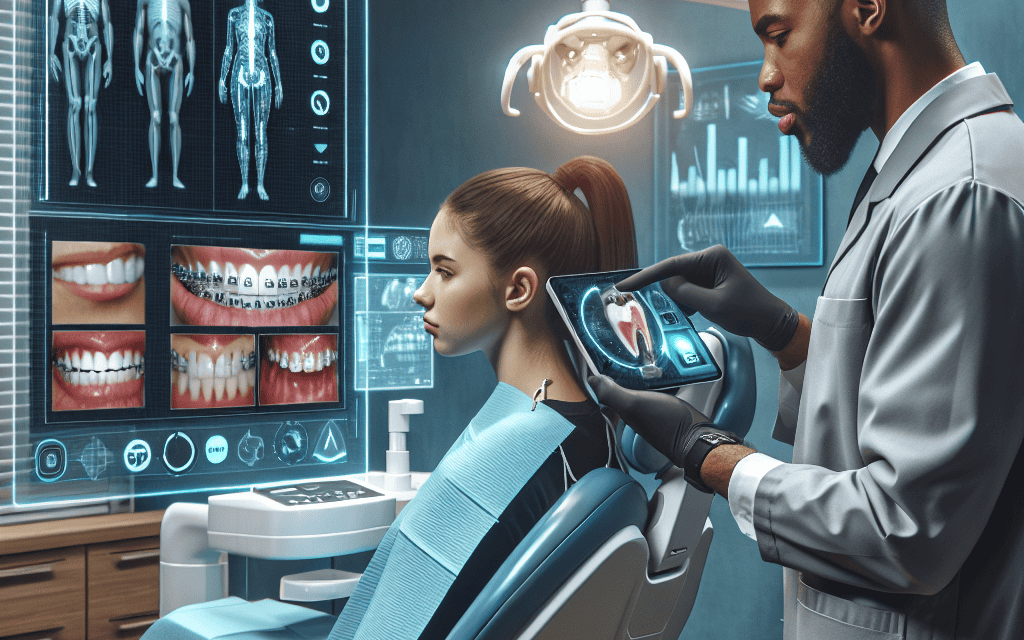
Revolutionizing Orthodontics with Remote Monitoring and Digital Technology
The field of orthodontics has undergone significant transformations over the past few decades, driven by advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on patient-centered care. Remote monitoring and digital technology are at the forefront of this revolution, offering innovative solutions that enhance treatment efficiency, improve patient outcomes, and streamline practice management. This article delves into the various aspects of how remote monitoring and digital technology are reshaping orthodontics, exploring their benefits, challenges, and future potential.
The Rise of Remote Monitoring in Orthodontics
Remote monitoring in orthodontics refers to the use of digital tools and technologies to track a patient’s progress outside of traditional in-office visits. This approach has gained traction due to its ability to provide real-time feedback and enhance patient engagement.
1.1 Understanding Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring involves the use of various digital devices and applications that allow orthodontists to monitor treatment progress without requiring patients to visit the office frequently. This can include:
- Smartphone applications that allow patients to send images of their teeth.
- Wearable devices that track oral health metrics.
- Telehealth platforms that facilitate virtual consultations.
By leveraging these technologies, orthodontists can assess treatment efficacy, make timely adjustments, and provide personalized care, all while minimizing the need for in-person appointments.
1.2 Benefits of Remote Monitoring
The benefits of remote monitoring in orthodontics are manifold:
- Increased Convenience: Patients can manage their treatment from the comfort of their homes, reducing travel time and associated costs.
- Enhanced Engagement: Regular check-ins and feedback can motivate patients to adhere to their treatment plans.
- Improved Outcomes: Early detection of issues can lead to timely interventions, potentially reducing treatment duration.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Fewer in-office visits can lower overall treatment costs for both patients and providers.
For instance, a study published in the “American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics” found that patients using remote monitoring tools reported higher satisfaction levels and better adherence to treatment protocols compared to those receiving traditional care.
1.3 Case Studies: Successful Implementation
Several orthodontic practices have successfully integrated remote monitoring into their workflows. For example, a practice in California implemented a remote monitoring system that allowed patients to submit weekly photos of their teeth. The orthodontist could then assess progress and provide feedback without requiring an office visit. This approach not only improved patient satisfaction but also reduced the average treatment time by 20%.
Another case study from a practice in New York highlighted the use of a telehealth platform for virtual consultations. Patients could discuss their concerns and receive professional advice without the need for an in-person appointment. This flexibility was particularly beneficial during the COVID-19 pandemic, when many patients were hesitant to visit healthcare facilities.
1.4 Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, remote monitoring in orthodontics is not without challenges:
- Technology Barriers: Not all patients may have access to the necessary technology or be comfortable using it.
- Data Privacy Concerns: The collection and storage of patient data raise important privacy and security issues.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The use of telehealth and remote monitoring is subject to varying regulations across different regions.
Addressing these challenges requires orthodontic practices to invest in training, ensure compliance with regulations, and prioritize patient education to foster confidence in using digital tools.
1.5 The Future of Remote Monitoring
The future of remote monitoring in orthodontics looks promising. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect:
- Increased integration of artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze patient data and predict treatment outcomes.
- Enhanced user interfaces for patient engagement and education.
- Broader acceptance and adoption of telehealth services across the healthcare landscape.
Ultimately, remote monitoring has the potential to become a standard practice in orthodontics, offering a more personalized and efficient approach to patient care.
Digital Technology: Transforming Orthodontic Treatment
Digital technology encompasses a wide range of tools and innovations that are transforming orthodontic treatment. From 3D imaging to computer-aided design (CAD), these technologies are enhancing precision and efficiency in orthodontic care.
2.1 3D Imaging and Scanning
3D imaging and scanning technologies have revolutionized the way orthodontists diagnose and plan treatments. Traditional impressions can be uncomfortable and imprecise, but digital scanning offers a more accurate and patient-friendly alternative.
- Intraoral Scanners: These devices capture detailed 3D images of a patient’s teeth and gums, allowing for precise treatment planning.
- CBCT Imaging: Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) provides comprehensive 3D images of the dental and skeletal structures, aiding in complex cases.
Research has shown that digital impressions reduce the likelihood of retakes and improve patient comfort. A study published in the “Journal of Clinical Orthodontics” found that patients preferred digital impressions over traditional methods, citing less discomfort and quicker procedures.
2.2 Computer-Aided Design and Manufacturing (CAD/CAM)
CAD/CAM technology allows orthodontists to design and manufacture custom appliances with unparalleled precision. This technology streamlines the workflow, reducing the time from diagnosis to treatment initiation.
- Custom Aligners: CAD/CAM enables the creation of personalized clear aligners that fit each patient’s unique dental anatomy.
- 3D Printing: Orthodontic practices can use 3D printing to produce models, retainers, and other appliances in-house, reducing costs and turnaround times.
A case study from a leading orthodontic practice demonstrated that the use of CAD/CAM technology reduced appliance fabrication time by 50%, allowing for quicker adjustments and improved patient satisfaction.
2.3 Virtual Treatment Planning
Virtual treatment planning software allows orthodontists to simulate treatment outcomes before initiating any procedures. This technology enhances communication with patients and helps set realistic expectations.
- Predictive Modeling: Orthodontists can visualize how teeth will move over time, allowing for more accurate treatment planning.
- Patient Education: Virtual simulations can help patients understand their treatment journey, increasing their engagement and compliance.
Research indicates that patients who are involved in the treatment planning process are more likely to adhere to their prescribed plans. A study published in “Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research” found that patients who viewed virtual treatment simulations reported higher satisfaction levels with their treatment outcomes.
2.4 Integration with Practice Management Software
Digital technology also extends to practice management software, which streamlines administrative tasks and enhances patient communication. Features may include:
- Appointment scheduling and reminders.
- Billing and insurance processing.
- Patient communication tools, such as text messaging and email notifications.
By integrating these tools, orthodontic practices can improve operational efficiency and enhance the overall patient experience. A survey conducted by the American Association of Orthodontists found that practices using integrated management software reported a 30% increase in patient retention rates.
2.5 The Future of Digital Technology in Orthodontics
The future of digital technology in orthodontics is bright, with ongoing advancements expected to further enhance treatment outcomes. Key trends include:
- Increased use of AI for predictive analytics and treatment optimization.
- Greater integration of virtual reality (VR) for patient education and engagement.
- Expansion of teleorthodontics, allowing for remote consultations and follow-ups.
As these technologies continue to evolve, orthodontists will be better equipped to provide personalized, efficient, and effective care to their patients.
Enhancing Patient Experience through Digital Solutions
In today’s competitive healthcare landscape, providing an exceptional patient experience is paramount. Digital solutions play a crucial role in enhancing patient satisfaction and engagement in orthodontics.
3.1 Patient-Centric Communication
Effective communication is essential for building trust and rapport with patients. Digital tools facilitate seamless communication between orthodontists and patients, ensuring that concerns are addressed promptly.
- Patient Portals: Secure online portals allow patients to access their treatment information, schedule appointments, and communicate with their orthodontist.
- Text Messaging Services: Automated reminders and updates via text message can improve appointment attendance and reduce no-shows.
A study published in the “Journal of Dental Research” found that practices utilizing patient portals experienced a 25% increase in patient engagement and satisfaction. Patients appreciated the convenience of accessing their information online and the ability to communicate easily with their providers.
3.2 Personalized Treatment Plans
Digital technology enables orthodontists to create personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s unique needs and preferences. This customization enhances the patient experience by ensuring that treatment aligns with individual goals.
- Custom Aligners: Digital scanning and CAD/CAM technology allow for the creation of aligners that fit perfectly, improving comfort and effectiveness.
- Flexible Treatment Options: Patients can choose from various treatment modalities, including traditional braces, clear aligners, or hybrid approaches.
Research indicates that patients who receive personalized treatment plans are more likely to adhere to their prescribed protocols. A survey conducted by the American Journal of Orthodontics found that 85% of patients reported higher satisfaction levels when involved in the treatment planning process.
3.3 Gamification and Engagement Tools
Gamification is an innovative approach that incorporates game-like elements into the treatment process to enhance patient engagement. Digital platforms can reward patients for adhering to their treatment plans, attending appointments, and maintaining good oral hygiene.
- Reward Systems: Patients can earn points for completing tasks, which can be redeemed for discounts or prizes.
- Progress Tracking: Visual progress tracking tools can motivate patients to stay on track with their treatment goals.
A case study from a dental practice that implemented gamification reported a 40% increase in patient compliance and engagement. Patients enjoyed the interactive elements and felt more invested in their treatment journey.
3.4 Telehealth for Enhanced Access
Telehealth services have become increasingly important in providing access to orthodontic care, especially for patients in remote or underserved areas. Virtual consultations allow patients to receive expert advice without the need for travel.
- Accessibility: Telehealth can bridge the gap for patients who may have difficulty accessing in-person care due to distance or mobility issues.
- Convenience: Patients can schedule virtual appointments at their convenience, reducing barriers to care.
A study published in the “Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare” found that telehealth consultations in orthodontics resulted in high patient satisfaction rates, with 90% of participants reporting a positive experience. This approach has proven particularly valuable during the COVID-19 pandemic, when many patients were hesitant to visit healthcare facilities.
3.5 The Future of Patient Experience in Orthodontics
The future of patient experience in orthodontics will likely be shaped by ongoing advancements in digital technology. Key trends to watch include:
- Increased use of AI-driven chatbots for patient inquiries and support.
- Enhanced virtual reality experiences for patient education and treatment visualization.
- Greater emphasis on patient feedback and data analytics to continuously improve care delivery.
As orthodontic practices embrace these innovations, they will be better positioned to provide exceptional patient experiences that foster loyalty and satisfaction.
Challenges and Considerations in Adopting Digital Technologies
While the benefits of remote monitoring and digital technology in orthodontics are clear, there are also challenges and considerations that practices must address when adopting these innovations.
4.1 Financial Investment and Cost-Benefit Analysis
Implementing digital technologies often requires a significant financial investment. Orthodontic practices must carefully evaluate the costs associated with purchasing equipment, software, and training staff.
- Initial Costs: The upfront costs of acquiring digital tools can be substantial, particularly for small practices.
- Ongoing Expenses: Maintenance, software subscriptions, and updates can add to the overall financial burden.
However, practices should also consider the long-term benefits of digital technology, including increased efficiency, improved patient satisfaction, and potential revenue growth. A cost-benefit analysis can help practices make informed decisions about technology investments.
4.2 Training and Staff Adaptation
The successful implementation of digital technologies requires adequate training for staff members. Orthodontic practices must invest time and resources into training their teams to effectively use new tools and systems.
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Staff should receive thorough training on how to use digital tools, interpret data, and communicate effectively with patients.
- Ongoing Support: Providing ongoing support and resources can help staff adapt to new technologies and address any challenges that arise.
A survey conducted by the American Dental Association found that practices that invested in staff training reported higher levels of staff satisfaction and improved patient outcomes. Ensuring that all team members are comfortable with digital tools is essential for successful implementation.
4.3 Data Privacy and Security Concerns
The collection and storage of patient data raise important privacy and security concerns. Orthodontic practices must prioritize data protection to maintain patient trust and comply with regulations.
- Compliance with Regulations: Practices must adhere to regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) to protect patient information.
- Data Security Measures: Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, such as encryption and secure access controls, is essential for safeguarding patient data.
A study published in the “Journal of Healthcare Management” found that practices with strong data security measures experienced fewer data breaches and higher patient trust levels. Prioritizing data privacy is crucial for maintaining a positive reputation in the digital age.
4.4 Patient Acceptance and Engagement
While many patients embrace digital technology, some may be hesitant to adopt new tools or may lack the necessary skills. Orthodontic practices must consider patient acceptance when implementing digital solutions.
- Patient Education: Providing clear information about the benefits of digital tools can help alleviate concerns and encourage adoption.
- Support for Technology Use: Offering assistance and resources for patients who may struggle with technology can enhance engagement.
A survey conducted by the American Association of Orthodontists found that 70% of patients expressed a preference for practices that offered digital solutions. By addressing patient concerns and providing support, practices can foster greater acceptance of digital technologies.
4.5 The Future of Digital Adoption in Orthodontics
The future of digital adoption in orthodontics will likely be shaped by ongoing advancements in technology and changing patient expectations. Key considerations include:
- Continued investment in training and education for both staff and patients.
- Ongoing evaluation of technology effectiveness and patient satisfaction.
- Adaptation to evolving regulations and data privacy standards.
As orthodontic practices navigate these challenges, they will be better positioned to leverage digital technologies to enhance patient care and improve operational efficiency.
The Future of Orthodontics: A Digital Transformation
The integration of remote monitoring and digital technology in orthodontics represents a significant shift in how care is delivered. As the field continues to evolve, several key trends are likely to shape the future of orthodontic practice.
5.1 Increased Personalization of Care
The future of orthodontics will see an even greater emphasis on personalized care. Digital technologies enable orthodontists to tailor treatment plans to each patient’s unique needs, preferences, and goals.
- Data-Driven Insights: Advanced analytics will allow orthodontists to make informed decisions based on individual patient data.
- Customized Treatment Options: Patients will have access to a wider range of treatment modalities, including hybrid approaches that combine traditional braces with clear aligners.
A study published in the “American Journal of Orthodontics” found that personalized treatment plans resulted in higher patient satisfaction and improved treatment outcomes. As technology continues to advance, orthodontists will be better equipped to provide tailored care that meets the unique needs of each patient.
5.2 Enhanced Collaboration Among Providers
The future of orthodontics will also see increased collaboration among healthcare providers. Digital technologies facilitate communication and information sharing, allowing orthodontists to work more closely with general dentists, oral surgeons, and other specialists.
- Interdisciplinary Care: Collaborative treatment planning can lead to more comprehensive care for patients with complex needs.
- Shared Digital Platforms: Cloud-based systems will enable providers to access and share patient information seamlessly.
A case study from a multi-disciplinary dental practice demonstrated that enhanced collaboration among providers led to improved patient outcomes and satisfaction. By working together, providers can ensure that patients receive holistic care that addresses all aspects of their oral health.
5.3 The Role of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to play a transformative role in orthodontics. AI-driven tools can analyze patient data, predict treatment outcomes, and optimize treatment plans.
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can identify patterns in patient data, allowing orthodontists to make data-driven decisions about treatment.
- Automated Workflow: AI can streamline administrative tasks, freeing up time for orthodontists to focus on patient care.
A study published in the “Journal of Dental Research” found that AI-driven tools improved treatment planning accuracy and reduced the time required for case analysis. As AI technology continues to advance, orthodontists will be better equipped to provide efficient and effective care.
5.4 Teleorthodontics as a Standard Practice
Teleorthodontics is likely to become a standard practice in the field, offering patients greater access to care and convenience. Virtual consultations and remote monitoring will enable orthodontists to provide ongoing support without the need for frequent in-office visits.
- Expanded Access: Teleorthodontics will bridge the gap for patients in remote or underserved areas, ensuring that everyone has access to quality care.
- Improved Patient Engagement: Regular virtual check-ins can enhance patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
A survey conducted by the American Association of Orthodontists found that 80% of patients expressed interest in teleorthodontic services. As practices embrace this model, they will be better positioned to meet the evolving needs of their patients.
5.5 Conclusion: Embracing the Digital Future
The integration of remote monitoring and digital technology in orthodontics represents a paradigm shift in how care is delivered. As practices embrace these innovations, they will be better equipped to provide personalized, efficient, and effective care that meets the needs of today’s patients.
Key takeaways from this exploration include:
- Remote monitoring enhances patient engagement and improves treatment outcomes.
- Digital technologies, such as 3D imaging and CAD/CAM, streamline workflows and enhance precision in treatment planning.
- Patient experience is significantly improved through personalized care, effective communication, and gamification strategies.
- Challenges related to financial investment, training, data privacy, and patient acceptance must be addressed for successful implementation.
- The future of orthodontics will be shaped by increased personalization, collaboration among providers, the role of AI, teleorthodontics, and ongoing advancements in digital technology.
As the orthodontic landscape continues to evolve, embracing these digital innovations will be essential for practices seeking to enhance patient care and remain competitive in an increasingly digital world.