Enhancing Telemedicine with Interactive 3D Pathology Visuals
Telemedicine has revolutionized healthcare delivery, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. As healthcare providers and patients increasingly rely on virtual consultations, the integration of advanced technologies becomes crucial. One such innovation is the use of interactive 3D pathology visuals, which can significantly enhance the telemedicine experience. This article explores the various dimensions of this integration, including its benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
The Evolution of Telemedicine
Telemedicine has evolved from simple telephone consultations to sophisticated digital platforms that allow for real-time video interactions, remote monitoring, and even virtual reality applications. The journey of telemedicine can be categorized into several key phases:
- Early Beginnings: The concept of telemedicine dates back to the 1920s when radio was used to transmit medical information. However, it wasn’t until the advent of the internet in the 1990s that telemedicine began to gain traction.
- Technological Advancements: The introduction of high-speed internet, smartphones, and telehealth platforms has made it easier for healthcare providers to offer remote consultations.
- COVID-19 Impact: The pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, with many healthcare systems implementing virtual visits to minimize the risk of virus transmission.
- Current Trends: Today, telemedicine encompasses a wide range of services, including mental health support, chronic disease management, and specialty consultations.
As telemedicine continues to evolve, the integration of interactive 3D pathology visuals represents a significant leap forward, enhancing the quality of care and patient engagement.
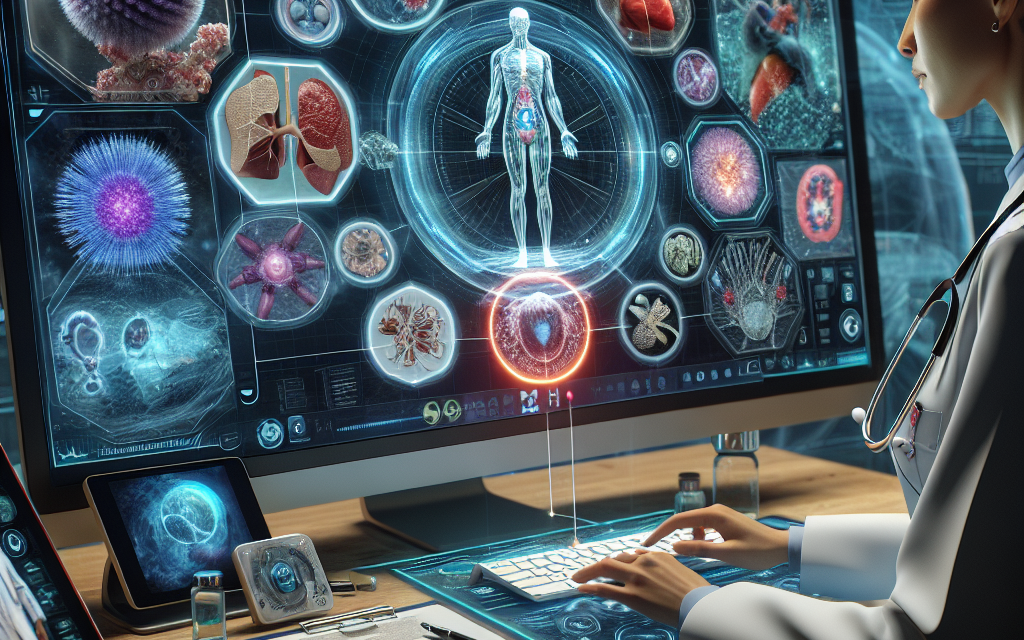
Understanding Interactive 3D Pathology Visuals
Interactive 3D pathology visuals are digital representations of pathological specimens that allow users to explore and manipulate the images in three dimensions. These visuals can be generated from various imaging techniques, including:
- Histopathology: The study of tissue samples under a microscope, often used to diagnose diseases like cancer.
- Radiology: Imaging techniques such as CT scans and MRIs that provide detailed views of internal structures.
- Molecular Pathology: The examination of molecules within tissues to understand disease mechanisms.
These visuals can be accessed through telemedicine platforms, allowing healthcare providers to share them with patients during virtual consultations. The interactive nature of these visuals enables users to:
- Rotate and zoom in on specific areas of interest.
- Highlight particular features or abnormalities.
- Access additional information, such as diagnostic criteria or treatment options.
The ability to interact with 3D pathology visuals enhances the educational aspect of telemedicine, empowering patients to better understand their conditions and treatment plans.
Benefits of Interactive 3D Pathology Visuals in Telemedicine
The integration of interactive 3D pathology visuals into telemedicine offers numerous benefits for both healthcare providers and patients. Some of the most significant advantages include:
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Interactive visuals allow patients to take an active role in their healthcare. By visualizing their conditions, patients can ask informed questions and participate in decision-making.
- Improved Diagnostic Accuracy: Healthcare providers can use 3D visuals to better understand complex cases, leading to more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
- Remote Collaboration: Specialists can collaborate remotely by sharing 3D visuals, facilitating second opinions and multidisciplinary discussions.
- Educational Opportunities: Medical professionals can use these visuals for training and education, enhancing their understanding of pathology and improving patient care.
- Accessibility: Patients in remote areas can access high-quality pathology visuals without the need for travel, making specialized care more accessible.
For example, a study published in the journal “Telemedicine and e-Health” found that patients who viewed 3D pathology visuals during consultations reported higher satisfaction levels and a better understanding of their conditions compared to those who received traditional 2D images.
Challenges in Implementing Interactive 3D Pathology Visuals
Despite the numerous benefits, the implementation of interactive 3D pathology visuals in telemedicine is not without challenges. Some of the key obstacles include:
- Technical Limitations: High-quality 3D visuals require advanced imaging technology and software, which may not be available in all healthcare settings.
- Training Requirements: Healthcare providers need training to effectively use and interpret 3D visuals, which can be a barrier to adoption.
- Data Privacy Concerns: The sharing of sensitive patient information through digital platforms raises concerns about data security and privacy.
- Cost Implications: The development and maintenance of 3D visualization technology can be costly, potentially limiting its widespread adoption.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Ensuring that 3D visuals can be seamlessly integrated into existing telemedicine platforms and electronic health records is crucial for effective implementation.
Addressing these challenges requires collaboration between technology developers, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies to create a framework that supports the safe and effective use of interactive 3D pathology visuals in telemedicine.
Future Prospects of Interactive 3D Pathology Visuals in Telemedicine
The future of interactive 3D pathology visuals in telemedicine is promising, with several trends and innovations on the horizon. Some potential developments include:
- Advancements in Imaging Technology: As imaging techniques continue to improve, the quality and detail of 3D pathology visuals will enhance, providing even more valuable insights for healthcare providers and patients.
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI algorithms can analyze 3D visuals to identify patterns and anomalies, assisting healthcare providers in making more accurate diagnoses.
- Virtual Reality Applications: The use of virtual reality (VR) technology can create immersive experiences for patients, allowing them to explore their conditions in a more engaging way.
- Personalized Medicine: 3D visuals can be tailored to individual patients, providing personalized insights into their specific conditions and treatment options.
- Global Collaboration: The ability to share 3D visuals across borders can facilitate international collaboration among healthcare providers, leading to improved patient outcomes worldwide.
As these trends continue to develop, the integration of interactive 3D pathology visuals into telemedicine will likely become more widespread, transforming the way healthcare is delivered and experienced.
Conclusion
The integration of interactive 3D pathology visuals into telemedicine represents a significant advancement in healthcare delivery. By enhancing patient engagement, improving diagnostic accuracy, and facilitating remote collaboration, these visuals can transform the telemedicine experience for both providers and patients. However, challenges such as technical limitations, training requirements, and data privacy concerns must be addressed to ensure successful implementation.
As technology continues to evolve, the future of interactive 3D pathology visuals in telemedicine looks promising. With advancements in imaging technology, AI integration, and personalized medicine, the potential for improved patient outcomes is immense. By embracing these innovations, healthcare providers can enhance the quality of care and empower patients to take an active role in their health journey.
In summary, the combination of telemedicine and interactive 3D pathology visuals has the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery, making it more accessible, engaging, and effective. As we move forward, it is essential to continue exploring and investing in these technologies to unlock their full potential for the benefit of patients and healthcare providers alike.