Essential Safety Features for Every Medical Facility
In the realm of healthcare, safety is paramount. Medical facilities, ranging from small clinics to large hospitals, must prioritize safety to protect patients, staff, and visitors. This article delves into the essential safety features that every medical facility should implement. By exploring these features, we aim to provide a comprehensive guide that ensures the well-being of all individuals within a healthcare environment.
1. Infection Control Measures
Infection control is a critical component of safety in medical facilities. The spread of infections can have dire consequences, leading to increased morbidity and mortality rates. Therefore, implementing robust infection control measures is essential.
1.1 Hand Hygiene Protocols
Hand hygiene is the cornerstone of infection control. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), proper hand hygiene can reduce the transmission of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) by up to 50%. Medical facilities must establish strict hand hygiene protocols, including the availability of hand sanitizers and regular training for staff.
Case studies have shown that facilities with rigorous hand hygiene practices experience significantly lower infection rates. For instance, a study conducted in a New York hospital demonstrated a 30% reduction in HAIs after implementing a comprehensive hand hygiene program.
1.2 Sterilization and Disinfection
Effective sterilization and disinfection practices are vital to prevent the spread of infections. Medical equipment and surfaces must be regularly cleaned and disinfected using appropriate agents. Facilities should adhere to guidelines provided by organizations such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to ensure compliance with best practices.
Statistics reveal that improper sterilization can lead to outbreaks of infections. For example, a 2018 outbreak of hepatitis C in a Texas clinic was traced back to inadequate sterilization of medical instruments, highlighting the importance of stringent sterilization protocols.
1.3 Isolation Rooms
Isolation rooms are designed to contain infectious patients and prevent the spread of pathogens. These rooms are equipped with specialized ventilation systems and negative pressure to ensure that airborne pathogens do not escape into other areas of the facility.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the importance of isolation rooms became evident. Facilities with well-designed isolation rooms were better equipped to handle infectious patients, reducing the risk of transmission to other patients and healthcare workers.
1.4 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PPE is a crucial component of infection control. Medical staff must have access to appropriate PPE, including masks, gloves, gowns, and face shields, to protect themselves and prevent the spread of infections.
The Ebola outbreak in West Africa underscored the importance of PPE. Healthcare workers who adhered to strict PPE protocols were less likely to contract the virus, emphasizing the need for adequate PPE supplies and training in medical facilities.
1.5 Vaccination Programs
Vaccination programs are essential for preventing the spread of infectious diseases within medical facilities. Staff should be vaccinated against common infections such as influenza and hepatitis B to protect themselves and their patients.
Research indicates that vaccination programs can significantly reduce the incidence of infections. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that healthcare facilities with comprehensive vaccination programs experienced a 40% reduction in influenza cases among staff and patients.
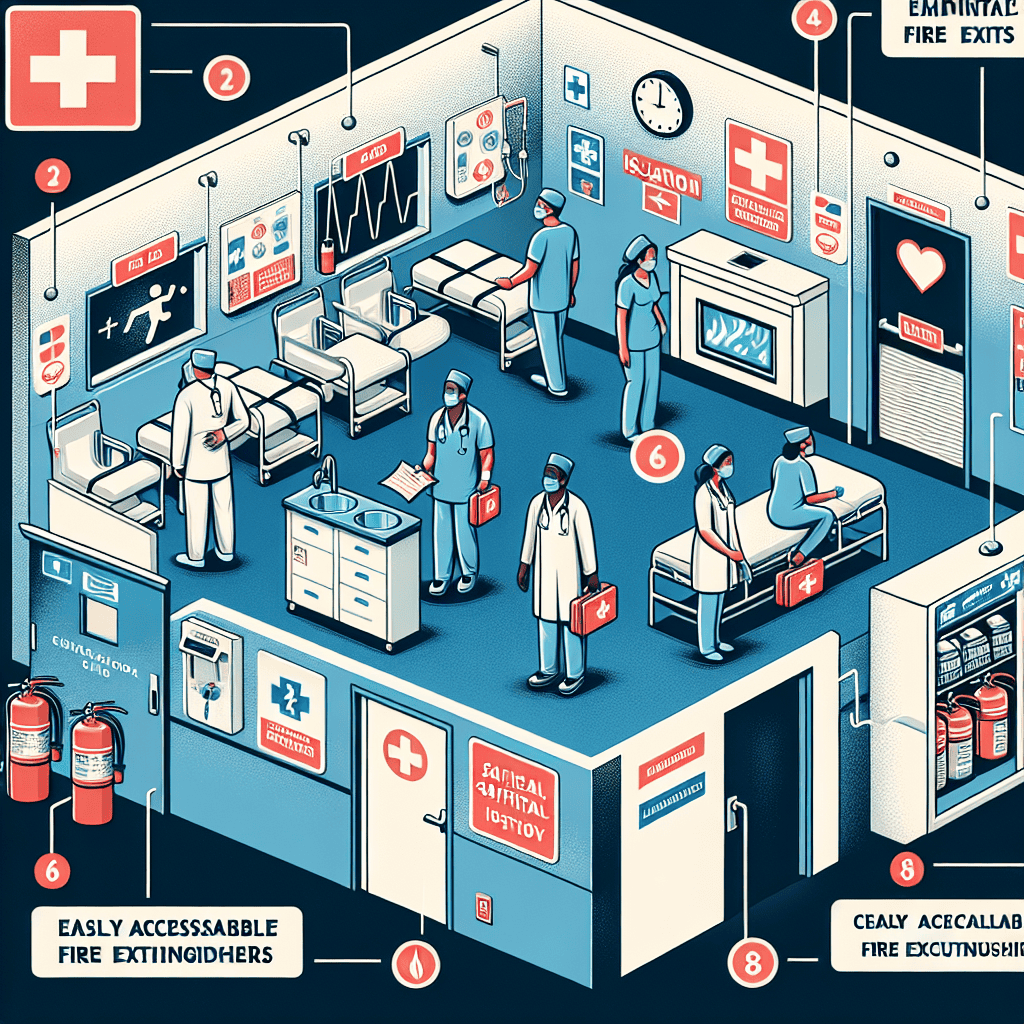
2. Fire Safety Systems
Fire safety is a critical concern in medical facilities due to the presence of flammable materials and equipment. Implementing effective fire safety systems is essential to protect lives and property.
2.1 Fire Detection and Alarm Systems
Fire detection and alarm systems are the first line of defense against fires. These systems should be regularly tested and maintained to ensure they function correctly in an emergency.
Statistics from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) indicate that facilities with well-maintained fire alarm systems experience fewer fire-related fatalities. For example, a study found that hospitals with functional fire alarms had a 50% lower mortality rate in fire incidents compared to those without.
2.2 Sprinkler Systems
Sprinkler systems are highly effective in controlling fires and preventing them from spreading. Medical facilities should install automatic sprinkler systems in all areas, including patient rooms, operating theaters, and storage areas.
Case studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of sprinkler systems in saving lives. In a 2019 fire at a California hospital, the sprinkler system activated promptly, containing the fire and allowing for the safe evacuation of patients and staff.
2.3 Fire Drills and Training
Regular fire drills and training sessions are essential to ensure that staff are prepared to respond effectively in the event of a fire. These drills should simulate real-life scenarios and involve all staff members, including medical, administrative, and support personnel.
Research shows that facilities that conduct regular fire drills have higher staff confidence and efficiency during actual fire emergencies. A study published in the Journal of Safety Research found that trained staff were 70% more likely to evacuate patients safely during a fire.
2.4 Fire Extinguishers and Emergency Exits
Fire extinguishers should be strategically placed throughout the facility and regularly inspected to ensure they are in working condition. Staff should be trained in the proper use of fire extinguishers to tackle small fires before they escalate.
Emergency exits must be clearly marked and free from obstructions. Facilities should conduct regular inspections to ensure that exit routes are accessible and that emergency lighting is functional.
2.5 Smoke Control Systems
Smoke control systems are designed to prevent the spread of smoke during a fire, allowing for safe evacuation. These systems include smoke barriers, ventilation systems, and smoke extraction fans.
During a fire, smoke inhalation is a leading cause of fatalities. Facilities with effective smoke control systems can significantly reduce the risk of smoke-related injuries and deaths. A study conducted by the NFPA found that hospitals with smoke control systems had a 60% lower incidence of smoke-related injuries during fires.
3. Electrical Safety
Electrical safety is a critical aspect of ensuring the safety of medical facilities. With the extensive use of electrical equipment and devices, it is essential to implement measures that prevent electrical hazards and ensure the safety of patients and staff.
3.1 Regular Electrical Inspections
Regular electrical inspections are crucial to identify potential hazards and ensure that all electrical systems are functioning correctly. Facilities should conduct routine inspections of electrical panels, wiring, and equipment to detect any signs of wear or damage.
Statistics from the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) indicate that regular inspections can reduce the risk of electrical fires by up to 30%. A case study from a hospital in Florida demonstrated that routine inspections helped identify faulty wiring, preventing a potential fire hazard.
3.2 Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs)
GFCIs are essential safety devices that protect against electrical shock by shutting off power when a ground fault is detected. Medical facilities should install GFCIs in areas with high moisture levels, such as bathrooms and kitchens, to prevent electrical accidents.
Research shows that GFCIs can reduce the risk of electrical shock by up to 80%. A study published in the Journal of Occupational Safety and Health found that facilities with GFCIs experienced significantly fewer electrical accidents compared to those without.
3.3 Surge Protection
Surge protection devices are crucial for safeguarding sensitive medical equipment from power surges and voltage spikes. Facilities should install surge protectors on all critical equipment to prevent damage and ensure uninterrupted operation.
Case studies have shown that facilities with surge protection experience fewer equipment failures and downtime. For example, a hospital in Texas reported a 40% reduction in equipment malfunctions after implementing a comprehensive surge protection program.
3.4 Electrical Safety Training
Electrical safety training is essential for all staff members to ensure they are aware of potential hazards and know how to respond in an emergency. Training should cover topics such as safe equipment handling, emergency procedures, and the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
Research indicates that facilities with comprehensive electrical safety training programs have lower rates of electrical accidents. A study conducted by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) found that trained staff were 50% less likely to experience electrical injuries compared to untrained personnel.
3.5 Backup Power Systems
Backup power systems, such as generators and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), are essential for ensuring the continuous operation of critical medical equipment during power outages. Facilities should regularly test and maintain backup power systems to ensure they function correctly when needed.
During natural disasters, backup power systems can be lifesaving. A case study from a hospital in Puerto Rico during Hurricane Maria demonstrated the importance of reliable backup power, as it allowed the facility to continue providing essential medical services despite widespread power outages.
4. Patient Safety Protocols
Patient safety is a fundamental aspect of healthcare, and medical facilities must implement protocols to protect patients from harm. These protocols encompass various aspects, including medication safety, fall prevention, and patient identification.
4.1 Medication Safety
Medication errors are a significant concern in healthcare, with the potential to cause serious harm to patients. Facilities should implement medication safety protocols, including electronic prescribing systems, barcode medication administration, and regular staff training.
Statistics from the Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP) indicate that facilities with robust medication safety protocols experience fewer medication errors. A study conducted in a hospital in California found a 30% reduction in medication errors after implementing an electronic prescribing system.
4.2 Fall Prevention
Falls are a common cause of injury in medical facilities, particularly among elderly patients. Facilities should implement fall prevention protocols, including risk assessments, bed alarms, and staff training on safe patient handling techniques.
Research shows that fall prevention programs can significantly reduce the incidence of falls. A study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society found that facilities with comprehensive fall prevention programs experienced a 40% reduction in fall-related injuries.
4.3 Patient Identification
Accurate patient identification is crucial to prevent medical errors and ensure patient safety. Facilities should implement protocols for verifying patient identity, such as using wristbands with barcodes and conducting regular audits to ensure compliance.
Case studies have demonstrated the importance of accurate patient identification. In a hospital in New York, a patient identification error led to a surgical procedure being performed on the wrong patient, highlighting the need for stringent identification protocols.
4.4 Infection Prevention
Infection prevention is a critical aspect of patient safety. Facilities should implement protocols for hand hygiene, sterilization, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) to prevent the spread of infections.
Statistics from the CDC indicate that facilities with robust infection prevention protocols experience lower rates of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). A study conducted in a hospital in Chicago found a 50% reduction in HAIs after implementing a comprehensive infection prevention program.
4.5 Communication and Handover Protocols
Effective communication and handover protocols are essential to ensure continuity of care and prevent errors. Facilities should implement standardized handover procedures, including the use of checklists and electronic health records (EHRs), to ensure accurate information transfer between healthcare providers.
Research shows that facilities with effective communication protocols experience fewer errors and improved patient outcomes. A study published in the Journal of Healthcare Management found that facilities with standardized handover procedures had a 30% reduction in communication-related errors.
5. Security Measures
Security is a critical aspect of safety in medical facilities, as it protects patients, staff, and property from potential threats. Implementing effective security measures is essential to ensure a safe and secure environment.
5.1 Access Control Systems
Access control systems are essential for regulating entry to sensitive areas within a medical facility. These systems can include key card access, biometric scanners, and security personnel to ensure that only authorized individuals can access restricted areas.
Case studies have shown that facilities with robust access control systems experience fewer security breaches. For example, a hospital in Los Angeles reported a 40% reduction in unauthorized access incidents after implementing a comprehensive access control system.
5.2 Surveillance Systems
Surveillance systems, including CCTV cameras and monitoring stations, are crucial for deterring criminal activity and ensuring the safety of patients and staff. Facilities should strategically place cameras in high-risk areas, such as entrances, parking lots, and emergency departments.
Research indicates that facilities with surveillance systems experience lower rates of crime. A study conducted by the International Association for Healthcare Security and Safety (IAHSS) found that hospitals with CCTV cameras had a 50% reduction in theft and vandalism incidents.
5.3 Security Personnel
Security personnel play a vital role in maintaining a safe environment within medical facilities. These individuals are responsible for monitoring access points, responding to security incidents, and ensuring the safety of patients and staff.
Statistics from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) indicate that facilities with security personnel experience fewer security incidents. A case study from a hospital in Chicago demonstrated that the presence of security personnel reduced the number of violent incidents by 30%.
5.4 Emergency Response Plans
Emergency response plans are essential for ensuring a coordinated and effective response to security incidents. Facilities should develop and regularly update these plans, which should include procedures for lockdowns, evacuations, and communication with law enforcement agencies.
Research shows that facilities with comprehensive emergency response plans experience improved outcomes during security incidents. A study published in the Journal of Emergency Management found that facilities with well-developed plans had a 40% reduction in response times during emergencies.
5.5 Visitor Management Systems
Visitor management systems are crucial for tracking and regulating the entry of visitors into medical facilities. These systems can include visitor badges, sign-in sheets, and electronic tracking systems to ensure that all visitors are accounted for.
Case studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of visitor management systems in enhancing security. A hospital in New York reported a 30% reduction in security incidents involving visitors after implementing an electronic visitor management system.
Conclusion
Ensuring safety in medical facilities is a multifaceted endeavor that requires the implementation of various essential safety features. From infection control measures to fire safety systems, electrical safety protocols, patient safety measures, and security systems, each aspect plays a crucial role in protecting patients, staff, and visitors.
By prioritizing these safety features, medical facilities can create a secure environment that promotes the well-being of all individuals within their care. As healthcare continues to evolve, it is imperative for facilities to stay informed about best practices and continuously improve their safety protocols to meet the ever-changing needs of the healthcare landscape.