Enhancing Dental Precision through 3D Scanning and Digital Imaging
The field of dentistry has undergone a significant transformation in recent years, largely due to advancements in technology. Among these advancements, 3D scanning and digital imaging have emerged as pivotal tools that enhance precision in dental practices. This article delves into the various aspects of how these technologies are revolutionizing dentistry, improving patient outcomes, and streamlining workflows. We will explore five key subtopics: the fundamentals of 3D scanning and digital imaging, their applications in various dental procedures, the benefits they offer to both practitioners and patients, challenges and limitations, and future trends in dental technology.
The Fundamentals of 3D Scanning and Digital Imaging
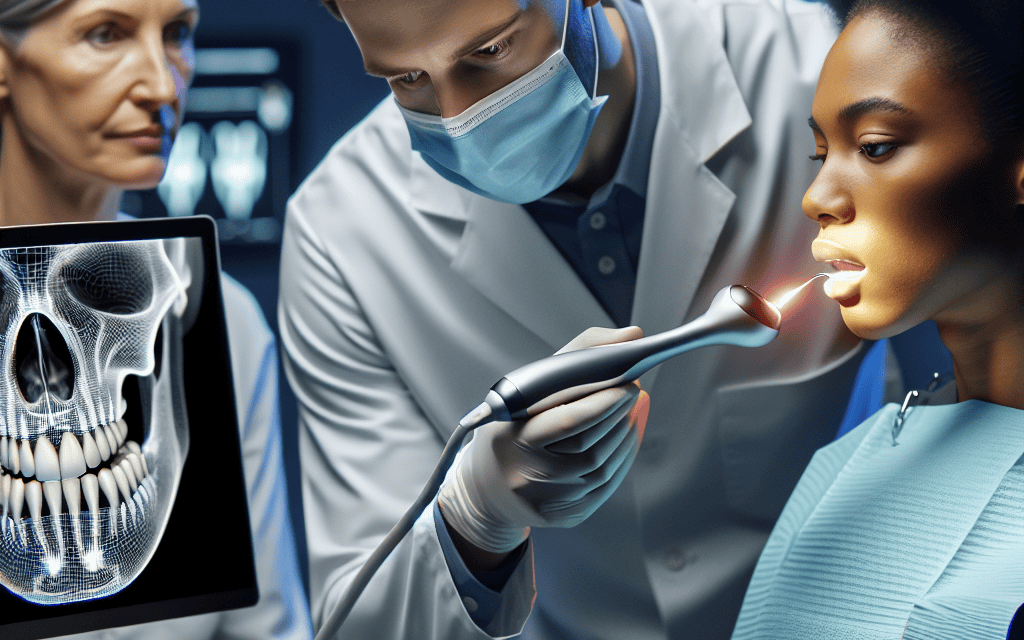
To understand the impact of 3D scanning and digital imaging in dentistry, it is essential to grasp the basic principles behind these technologies. 3D scanning involves capturing the physical dimensions of an object and converting them into a digital format. This process typically employs laser or optical scanning techniques to create a detailed three-dimensional representation of the scanned object.
Digital imaging, on the other hand, refers to the process of creating visual representations of the interior structures of the teeth and surrounding tissues. This can include techniques such as digital radiography, intraoral photography, and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). Together, these technologies provide a comprehensive view of a patient’s oral health, enabling more accurate diagnoses and treatment planning.
- 3D Scanning Techniques: Various methods are employed in 3D scanning, including laser scanning, structured light scanning, and contact scanning. Each method has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the dental procedure.
- Digital Imaging Techniques: Digital radiography is a common method that uses electronic sensors to capture images, significantly reducing radiation exposure compared to traditional X-rays. CBCT provides three-dimensional images that allow for detailed visualization of bone structures and dental anatomy.
- Integration with CAD/CAM: The data obtained from 3D scans and digital images can be integrated with computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems, facilitating the creation of precise dental restorations.
- Data Storage and Management: Digital images and 3D scans can be easily stored, retrieved, and shared among dental professionals, enhancing collaboration and improving patient care.
- Patient Engagement: Digital imaging allows for better communication with patients, as they can visually understand their dental conditions and treatment options through high-quality images.
Applications in Various Dental Procedures
The applications of 3D scanning and digital imaging in dentistry are vast and varied. These technologies are utilized in numerous procedures, ranging from diagnostics to treatment planning and execution. Here are some key areas where these technologies are making a significant impact:
- Orthodontics: 3D scanning is revolutionizing orthodontic treatment by allowing for precise measurements of dental arches and tooth positions. This data can be used to create custom aligners and braces that fit perfectly, improving treatment outcomes.
- Implantology: In dental implant procedures, 3D imaging provides detailed views of the jawbone structure, enabling accurate placement of implants. Surgeons can plan the procedure with precision, reducing the risk of complications.
- Restorative Dentistry: Digital impressions taken through 3D scanning eliminate the need for traditional impression materials, which can be uncomfortable for patients. This leads to more accurate restorations, such as crowns and bridges.
- Periodontics: 3D imaging allows for better assessment of periodontal conditions, enabling dentists to visualize bone loss and plan appropriate treatments.
- Oral Surgery: Surgeons can use 3D models created from scans to simulate surgical procedures, improving their ability to anticipate challenges and enhance patient safety.
For instance, a study published in the “American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics” highlighted that orthodontic treatments utilizing 3D imaging resulted in a 30% reduction in treatment time compared to traditional methods. This not only benefits the patient but also increases the efficiency of the dental practice.
Benefits for Practitioners and Patients
The integration of 3D scanning and digital imaging into dental practices offers numerous benefits for both practitioners and patients. These advantages contribute to improved clinical outcomes, enhanced patient experiences, and increased operational efficiency.
- Increased Accuracy: The precision of 3D scans and digital images minimizes the chances of errors in diagnosis and treatment planning. This leads to better-fitting restorations and more successful outcomes.
- Enhanced Patient Comfort: Digital impressions are often more comfortable than traditional methods, reducing gag reflexes and discomfort associated with impression materials.
- Time Efficiency: The speed of obtaining digital scans and images allows for quicker turnaround times in treatment planning and execution, benefiting both the dentist and the patient.
- Improved Communication: High-quality images facilitate better communication between dentists and patients, allowing for more informed decision-making regarding treatment options.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment in 3D scanning and digital imaging technology can be significant, the long-term savings from reduced chair time, fewer remakes, and improved patient satisfaction can outweigh these costs.
A case study involving a dental practice that adopted digital imaging technology reported a 25% increase in patient satisfaction scores. Patients appreciated the clarity of their treatment plans and the reduced discomfort associated with digital impressions. This not only improved patient retention but also attracted new clients through positive word-of-mouth.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the numerous benefits of 3D scanning and digital imaging, there are challenges and limitations that dental practitioners must navigate. Understanding these obstacles is crucial for successful implementation and utilization of these technologies.
- Initial Costs: The upfront investment for 3D scanning and digital imaging equipment can be substantial, which may deter some practices from adopting these technologies.
- Training Requirements: Dental professionals must undergo training to effectively use and interpret digital imaging and 3D scanning technologies. This can require time and resources that some practices may not have.
- Data Management: The storage and management of large digital files can pose challenges, particularly for smaller practices with limited IT infrastructure.
- Patient Acceptance: Some patients may be hesitant to embrace new technologies, preferring traditional methods they are more familiar with. Educating patients about the benefits of digital imaging is essential.
- Regulatory Considerations: Compliance with regulations regarding digital imaging and patient data security is critical. Practices must ensure they are adhering to legal standards to protect patient information.
For example, a survey conducted by the American Dental Association found that 40% of dental practices cited high initial costs as a significant barrier to adopting digital imaging technologies. Addressing these challenges requires strategic planning, investment in training, and effective communication with patients about the benefits of these advancements.
Future Trends in Dental Technology
The future of dentistry is poised for further transformation as technology continues to evolve. Several trends are emerging that will likely shape the landscape of dental practice in the coming years.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is expected to play a significant role in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning. Machine learning algorithms can analyze digital images and scans to identify potential issues that may be overlooked by human practitioners.
- Tele-dentistry: The rise of telehealth has extended to dentistry, allowing for remote consultations and follow-ups. Digital imaging can facilitate virtual assessments, improving access to care for patients in remote areas.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR technology may be integrated into dental practices to provide real-time visualizations during procedures, enhancing precision and outcomes.
- Personalized Dentistry: Advances in genomics and biotechnology may lead to more personalized treatment plans based on individual patient data, improving overall care.
- Sustainability Initiatives: As environmental concerns grow, dental practices may adopt more sustainable practices, including digital workflows that reduce waste associated with traditional materials.
For instance, a recent study published in the “Journal of Dental Research” highlighted the potential of AI in analyzing CBCT images, achieving diagnostic accuracy rates comparable to experienced radiologists. This indicates a promising future where technology can augment human expertise in dentistry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of 3D scanning and digital imaging into dental practices is revolutionizing the field, enhancing precision, improving patient experiences, and streamlining workflows. While challenges exist, the benefits far outweigh the limitations, making these technologies essential tools for modern dentistry. As we look to the future, advancements such as AI, tele-dentistry, and personalized care will further enhance the capabilities of dental professionals, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. Embracing these technologies is not just a trend; it is a necessary evolution in providing high-quality dental care in an increasingly digital world.